DiscoPygal is a suite of tools that enables rapid development of, and experimentation with, solutions for multi-robot motion planning problems in 2D and the visualization and verification of the resulting plans. It is written in Python and uses CGAL (Computational Geometry Algorithm Library) among other components. In Particular, it exploits the CGAL Python bindings of 2D arrangements, 2D Minkowski sums, and 2D Regularized Boolean Set Operations needed for the implementation of fundamental motion-planning algorithms.
The DiscoPygal suite is often delivered as python package when meant to be used for its functionality as an infrastructure for motion planning problems.
Abilities and functionality
Discopygal offers the following functionality:
- Implementing motion-planning algorithms
- Testing these algorithms on different scenes (also can visualize the scenes and solutions)
- Running automatically several experiments on different scenarios
Graphic Tools
For this use it consists of two parts:
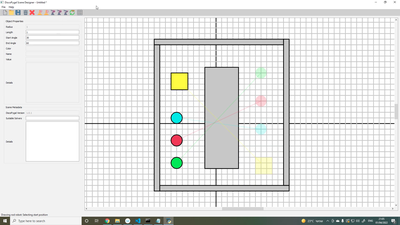
- The DiscoPygal Scene Editor Tool (called scene_designer) – enables the creation of scenes with polygonal or disk-shaped obstacles and robots;
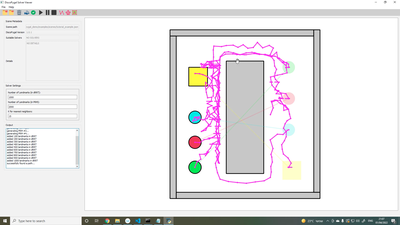
- The DiscoPygal Solver Tool (called solver_viewer) – solves motion planning problems, displays graphically the input scene, output paths, and configuration spaces and other intermediate states of the motion planning process; it can also simulate the solution. DiscoPygal enables the dynamic
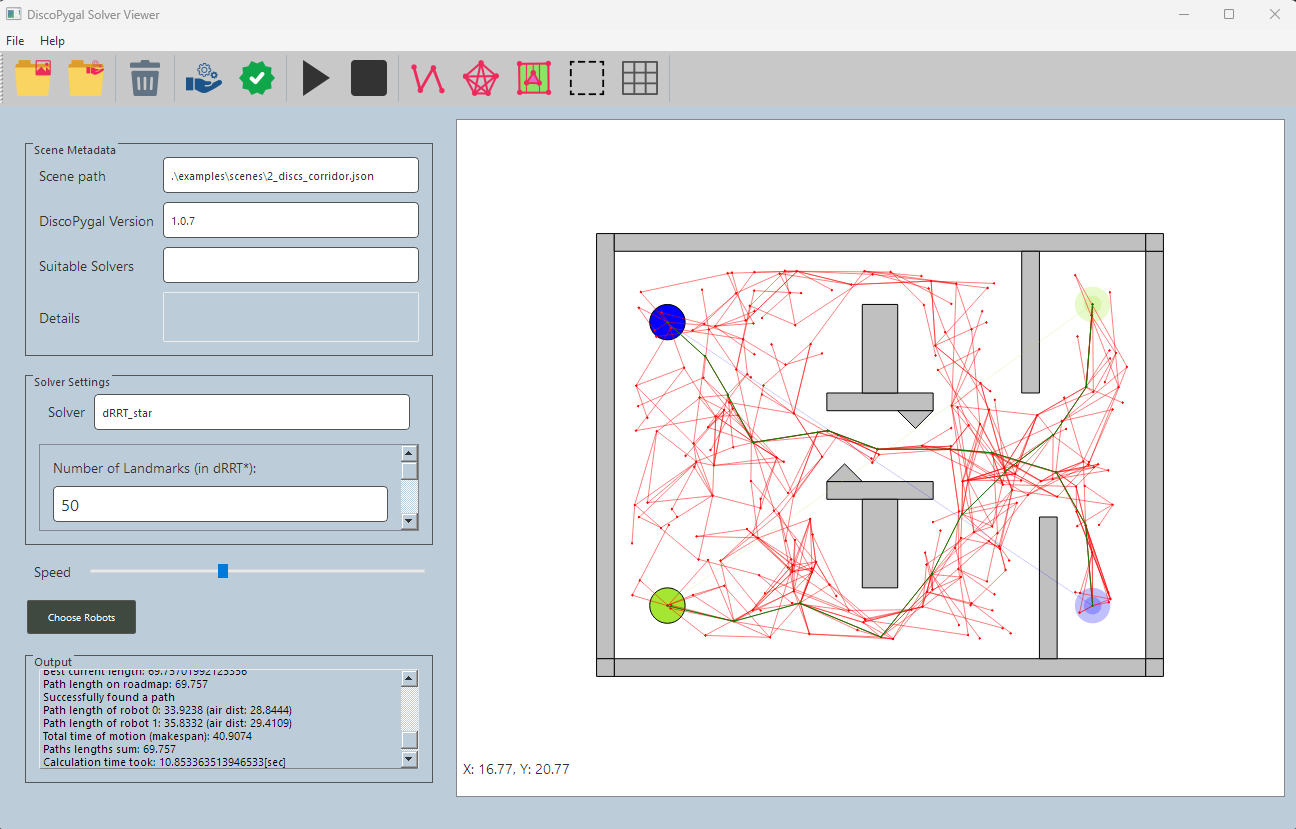
Screenshot from solver_viewer tool loading of motion-planning algorithms in the form of Python scripts during run time. It allows users to easily swap and compare between different motion-planning algorithms, and even modify an existing implementation of an algorithm while the program is running. (There is no need to recompile the code or restart the program.)
The code was originally developed by Nir Goren. Then, it was enhanced by Michael Bilevich and afterwards by Yuval Rubins who is currently maintaining it.
Links
Link to package documentation: https://www.cs.tau.ac.il/~cgl/discopygal/docs/
Link for getting started: https://www.cs.tau.ac.il/~cgl/discopygal/docs/tutorials/getting_started.html
Example
|
|
|
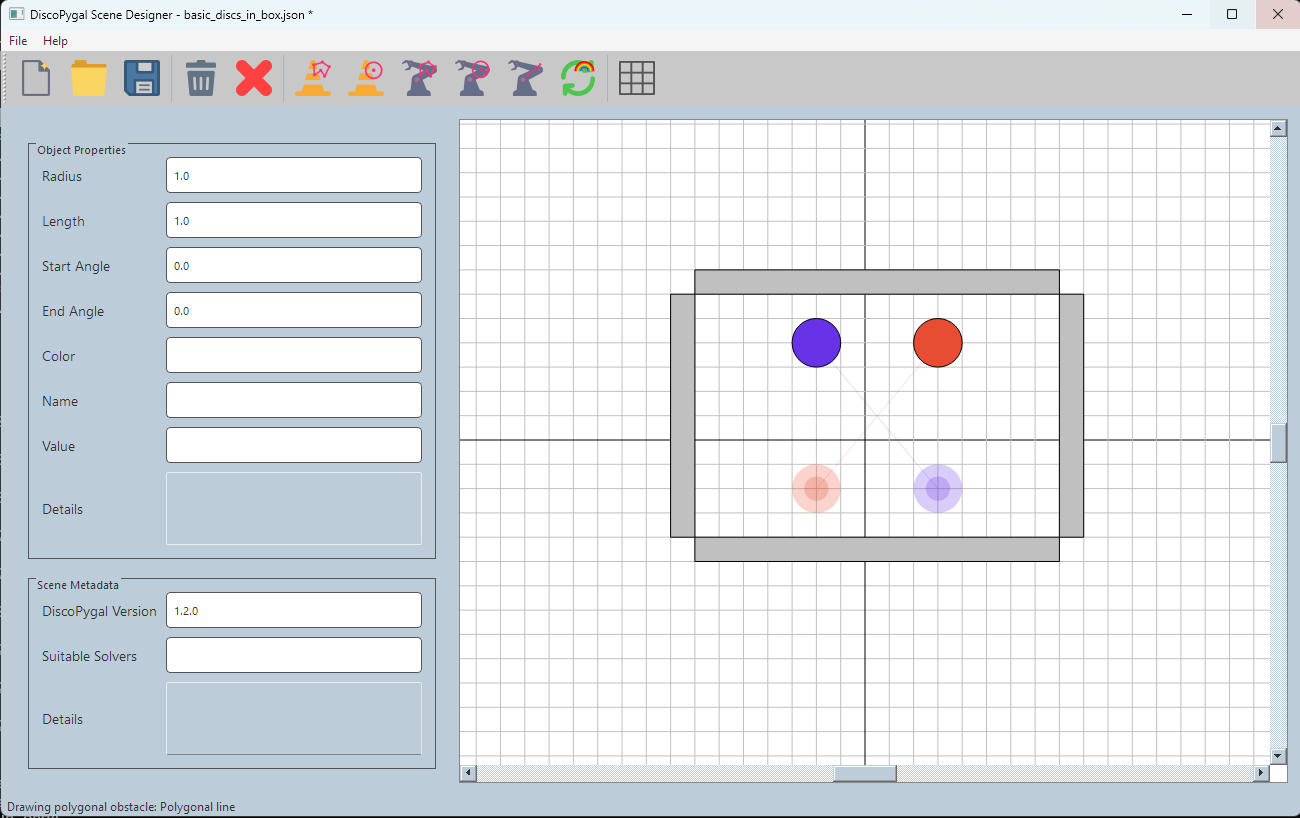
| An example of an input motion planning problem (a) and the output paths computed by DicoPygal (b). The input scene consists of four robots drawn in distinct colors. The solid shapes indicate the starting positions of the robots and the translucent shapes indicate the corresponding target positions. The objective is to plan a path for each robot from the starting position to the target position while avoiding collisions with the obstacles, drawn in gray, and with the other robots in the scene. The resulting paths are drawn in purple. | |